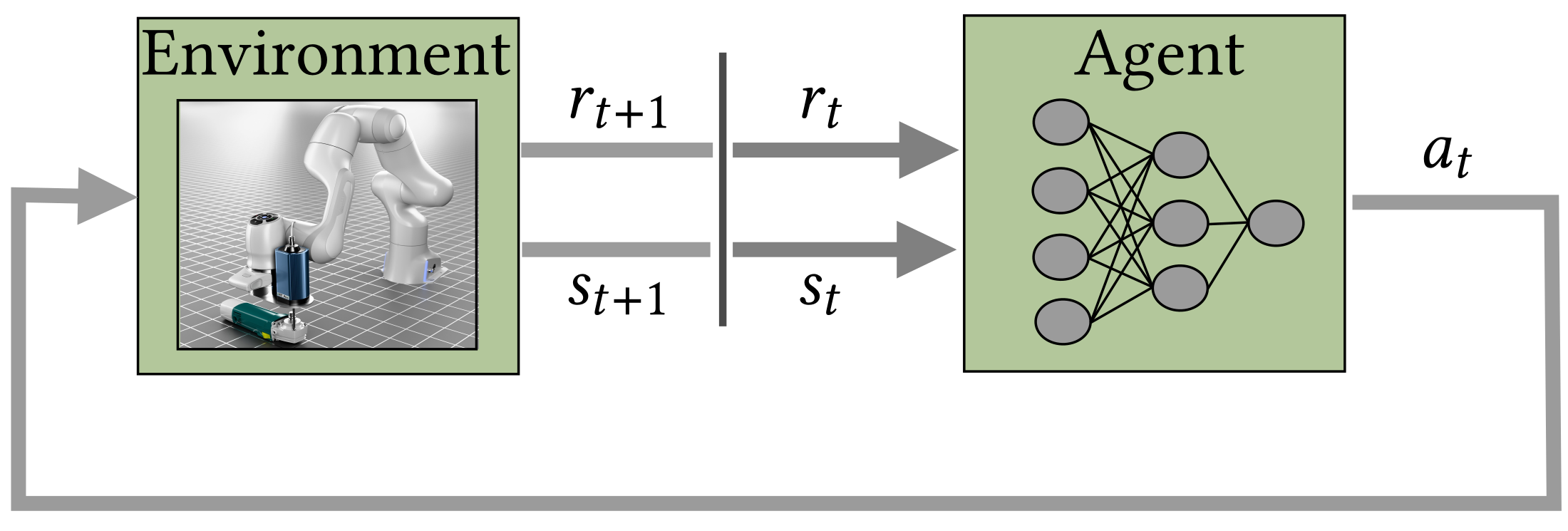
Reinforcement Learning
Our group works on reinforcement learning algorithms, where the goal is to optimize the parameters of a policy purely based on environment interaction. This learning paradigm is specifically interesting for robotic use cases because the robot can potentially learn solving problems autonomously. Our group focuses on several aspects in reinforcement learning.
One key question is how to represent the policy in RL in order to acquire skills that can solve complex tasks? A look into advances in supervised learning show that we need reinforcement learning algorithms that can train complex policy representations. These policy representations also include diffusion/flow based policies that have proven very successful in other supervised learning fields and are mostly part of big models such as in VLAs, but training them in the context of reinforcement learning is not straightforward.
Training these policies also requires improved exploration behavior in order to generate high-quality data points during training. One promising option for improved exploration is generating time-correlated actions during the exploration phase using action chunking, or motion primitives. The underlying policies have a drastically increased action space making the optimization in general more complex, which also requires specific RL algorithms for efficient training.
A very promising approach towards generalists policies is based on fine tuning existing foundation-model based policy representations. Vision-Language-Action (VLAs) policies have the potential to solve tasks where the instruction is text-based easying communication with humans. We believe that RL is a key approach in this field to enable robots adapting their generalist policies using reinforcement learning such that they can learn solving a task that is not part of their supervised training data set.
Key Areas
- Complex policy representations for reinforcement learning
- Time-correlated action selection using action chunking and motion primitives
- Fine-tuning of foundation models using reinforcement learning
Members
Andreas Boltres
Computer Networking, Geometric Deep Learning, Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
 Autonomous Learning Robots
Autonomous Learning Robots 





